Displaying Spectra
Because of its use of glue as the underlying data-handling layer and its applicability in several different contexts, Specviz takes a modular approach to displaying data that has been loaded.
The first spectrum you load will be automatically displayed in the viewer with the view window set by the extent of the spectrum. Additional spectra may not be fully shown if they exceed the bounds of the plotted area, which are set based on the first displayed spectrum. The bounds can be changed via the Pan/Zoom tool or by deselecting the current spectra and selecting a different spectrum for display.
Much of the Specviz functionality can be handled within the tool or the Jupyter notebook using an API. The Toolbar below gives you several spectroscopic display options. Right click will open a dropdown with access to different options for each button.
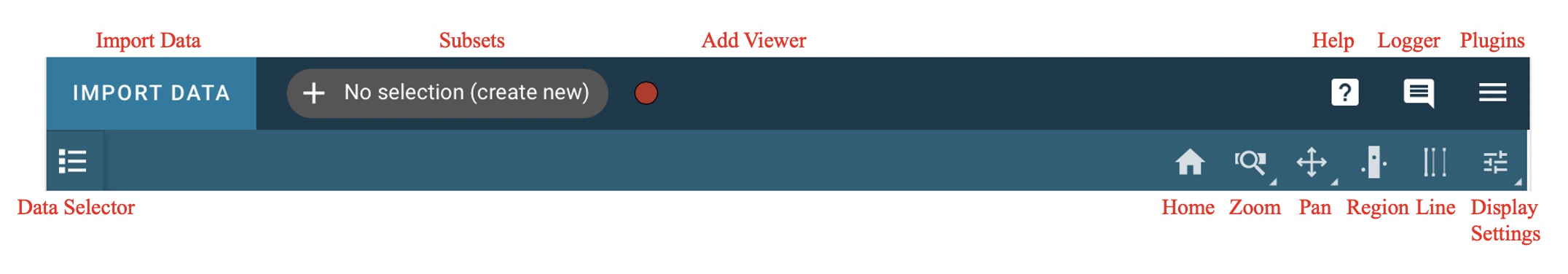
Selecting/Showing Data Sets
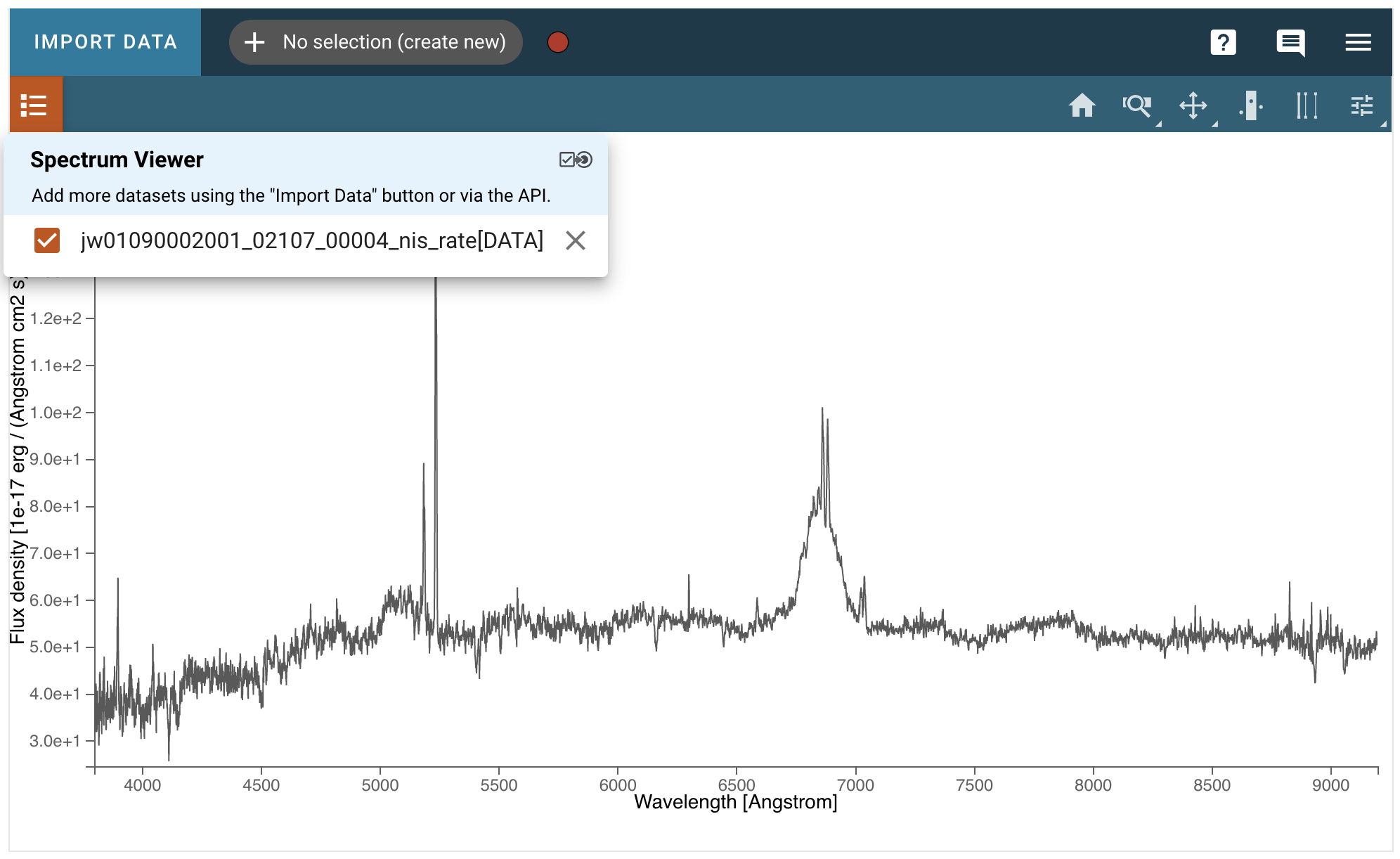
Data can be selected and de-selected in each viewer’s data menu, opened by clicking the
 button in the top left of the viewer. Here, you can click a
checkbox next to the listed data to make the data visible (checked) or invisible (unchecked).
button in the top left of the viewer. Here, you can click a
checkbox next to the listed data to make the data visible (checked) or invisible (unchecked).
In addition to toggling the visibility of a data layer, the data can be unloaded from a viewer by clicking the “x” button on the right. Data unloaded from the viewer will also be excluded as options from dataset dropdown menus in the various plugins. Unloaded data will be available to re-load into the viewer or remove permanently from the app from an expandable section in the data menu.
Cursor Information
By moving your cursor along the spectrum viewer, you will be able to see information on the cursor position as well as the spectral axis value, pixel, and flux of the closest data point to the cursor. This information is displayed in the top bar of the UI, on the middle-right side.
Home
This button will reset your zoom and panning to display the entire image.
Box Zoom
The  (box) and
(box) and  (x-range) zoom tools allow you to zoom by
clicking and dragging with your mouse. The box zoom tool adjusts both the x and y range of
the plot, whereas the x-range tool zooms only the x-axis to the selected region. While
clicking and dragging you will see the selected region as a gray box, as below.
(x-range) zoom tools allow you to zoom by
clicking and dragging with your mouse. The box zoom tool adjusts both the x and y range of
the plot, whereas the x-range tool zooms only the x-axis to the selected region. While
clicking and dragging you will see the selected region as a gray box, as below.
You can switch between the x-range zoom tool and the plot tool by right-clicking (or your trackpad equivalent) on the currently selected zoom icon on the viewer toolbar, which will open a menu of choices as in the screenshot below.
Pan Zoom
There are several ways to pan around a spectrum or zoom in on features of interest. Right click will open a dropdown with access to different options described below.
Interactive Pan/Zoom (Desktop or Notebook Interface)
You can find the following Pan/Zoom tools available in the viewer toolbar on the top right of the viewer.
Home
This button will reset your zoom and panning to display the spectrum.
Previous zoom is also available by right-clicking on the home icon and selecting the previous zoom icon. This will revert to the last saved zoom state. Zoom states are saved when beginning a zoom selection or when activating a pan/zoom tool.
2D Bidirectional Pan/Zoom
The  icon allows you to zoom using the scroll wheel.
The window will zoom into the area around your cursor.
To pan, simply click and drag the window.
icon allows you to zoom using the scroll wheel.
The window will zoom into the area around your cursor.
To pan, simply click and drag the window.
Horizontal/Vertical Zoom
The  (horizontal) and
(horizontal) and  (vertical) Zoom tools allow you to zoom along each axis, while locking the other. You can also zoom by scrolling.
(vertical) Zoom tools allow you to zoom along each axis, while locking the other. You can also zoom by scrolling.
From the API
The Specviz helper contains a set of convenience methods to programmatically define the view of the spectrum viewer. You may instantiate a Specviz Helper via:
from jdaviz import Specviz
# Instantiate an instance of Specviz
specviz = Specviz()
# Display Specviz
specviz.show()
Limit methods
You can use the methods x_limits() and
y_limits() to modify the field of
view of Specviz. You can provide a scalar (which assumes the units of the loaded spectra),
a Quantity, or 'auto' to automatically scale:
from astropy import units as u
specviz.x_limits()
specviz.x_limits(650*u.nm,750*u.nm)
specviz.y_limits('auto', 110.0)
Additionally, you can provide the limit methods with a SpectralRegion. Specviz shall set the bounds the upper and lower bounds of the SpectralRegion:
from specutils import SpectralRegion
bounds = SpectralRegion(0.45*u.nm, 0.6*u.nm)
specviz.x_limits(bounds)
Autoscale methods
You can also quickly return to the default zoom using
autoscale_x() and
autoscale_y().
Axis Orientation methods
To quickly flip an axis to change to and from ascending/descending, use
flip_x() and
flip_y().
Defining Spectral Regions
Spectral regions can be defined by clicking on the  icon at the right of the
viewer toolbar.
icon at the right of the
viewer toolbar.
To select a region of interest, move the cursor to one of the end points (in wavelength) of the region you want to select, and drag it to the other end point. The selected region background will display in light gray color, and the spectral trace in color, coded to subset number and listed under the subsets dropdown.
Clicking on that selector, you can add more regions by selecting the “create new” entry.
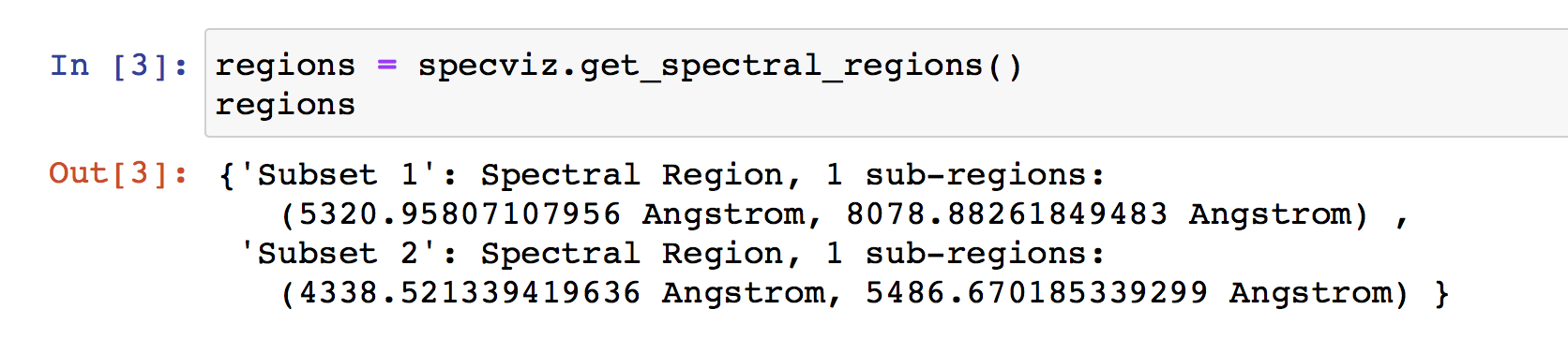
From the API, you can use the get_spectral_regions() method:
Line Selection
This button will allow you to click and select a vertical line when multiple lines from a line list are over-plotted. Futher analysis can be performed on this line of interest.
See also
- Line Lists
Documentation on using line lists within Specviz.
Plot Settings
To access plot settings for a particular viewer (including the spectrum viewer),
click the  icon in the viewer toolbar or open the
Plot Options plugin.
icon in the viewer toolbar or open the
Plot Options plugin.
Layer
The top section of the Layer tab contains options to change the color
of the spectrum (click the  icon to see a color change menu),
change visibility of the spectrum (
icon to see a color change menu),
change visibility of the spectrum ( icon), and a dropdown box to select
which layer will have its settings changed.
icon), and a dropdown box to select
which layer will have its settings changed.
Line Width
Width of the line for the spectrum in pixels. Larger values are thicker lines on the plot.
Line Opacity
Opacity of the line. Maximum (1) is fully opaque and minimum (0) is fully transparent.
Plot profile as steps
Toggle on to view the spectrum as a continuous line or a step function.
Plot uncertainties
Toggle on to view uncertainties attached to the spectrum, if any.
From the API
plot_options = specviz.plugins['Plot Options']
plot_options.uncertainty_visible = True